Sublimation Color Theory
Hi, my name is Chris. I have been working in Vietnam since 2008. Yes, understanding the basics of color theory is a prerequisite for sublimation printing in Vietnam. Color is caused by light striking an object and being reflected back to the eye. We define color using three words: hue, saturation and brightness.
Hue: the name we give to a color
Saturation: vividness of the color
Brightness: lightness or darkness of the color
If you plan to do your sublimation printing in Vietnam then I recommend understanding the basics of color theory.
Hue: the name we give to a color
Saturation: vividness of the color
Brightness: lightness or darkness of the color
If you plan to do your sublimation printing in Vietnam then I recommend understanding the basics of color theory.

What is the bare minimum I need to know about color theory?
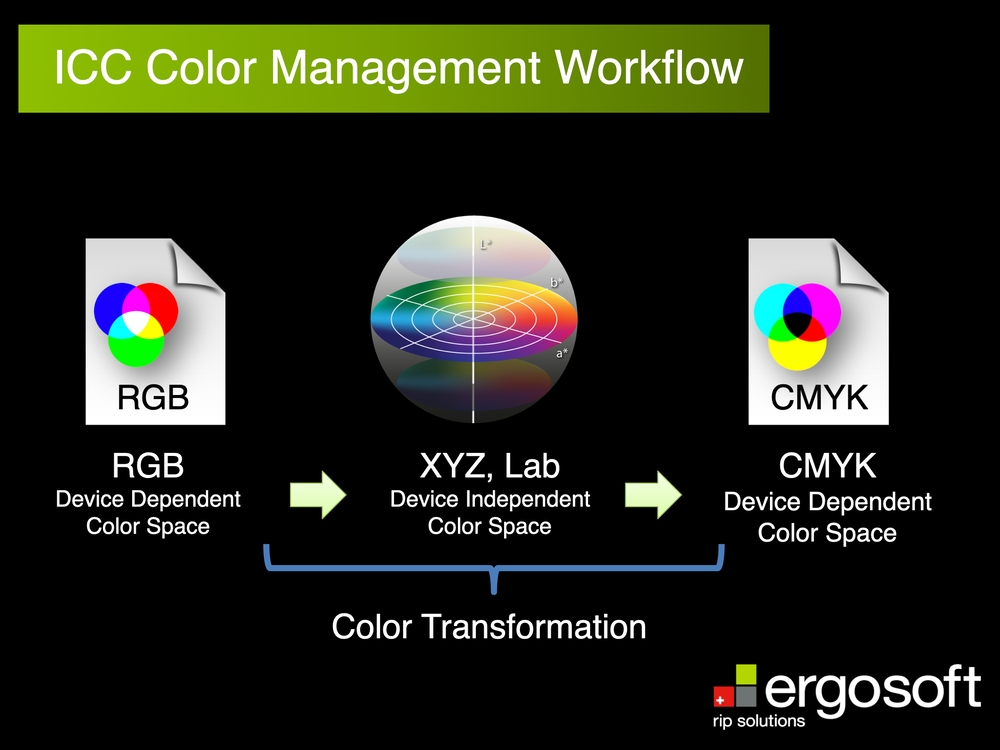
Understand the difference between these three color spaces LAB, RGB and CMYK. Understand that what you see on a computer screen is not what you will see on the printed paper nor the fabric once printing is done. Matching the screen colors with the final print colors requires expertise. Understand that Raster Image Processing (RIP) software translates digital images into printable dots which will optically mix to constitute the colors in the image. A good sublimation printing company must have educated and experience technicians who understand color theory, color spaces and the RIP process.
May I assist you with sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Understand the difference between these three color spaces LAB, RGB and CMYK. Understand that what you see on a computer screen is not what you will see on the printed paper nor the fabric once printing is done. Matching the screen colors with the final print colors requires expertise. Understand that Raster Image Processing (RIP) software translates digital images into printable dots which will optically mix to constitute the colors in the image. A good sublimation printing company must have educated and experience technicians who understand color theory, color spaces and the RIP process.
May I assist you with sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Produce sublimated garments in Vietnam?
Imagine that you have an idea to produce sublimated surf shorts, sports jerseys or mouse pads. Would it be great to get inside a sublimation apparel factory to see how they print and sew? Would you like to check the quality yourself? I can get you inside Vietnamese sublimation factories for a tour. Watch my video for more details.
Add your own artwork and player numbers



Should my printer us 4, 6 or 8 CMYK inks on their printers?
RGB stands for red, green and blue color space/model.
CMYK stands for cyan, magenta, yellow and black color space/model.
RGB is the color space you see on your computer screens.
CMYK is the color space you see used on your printers.
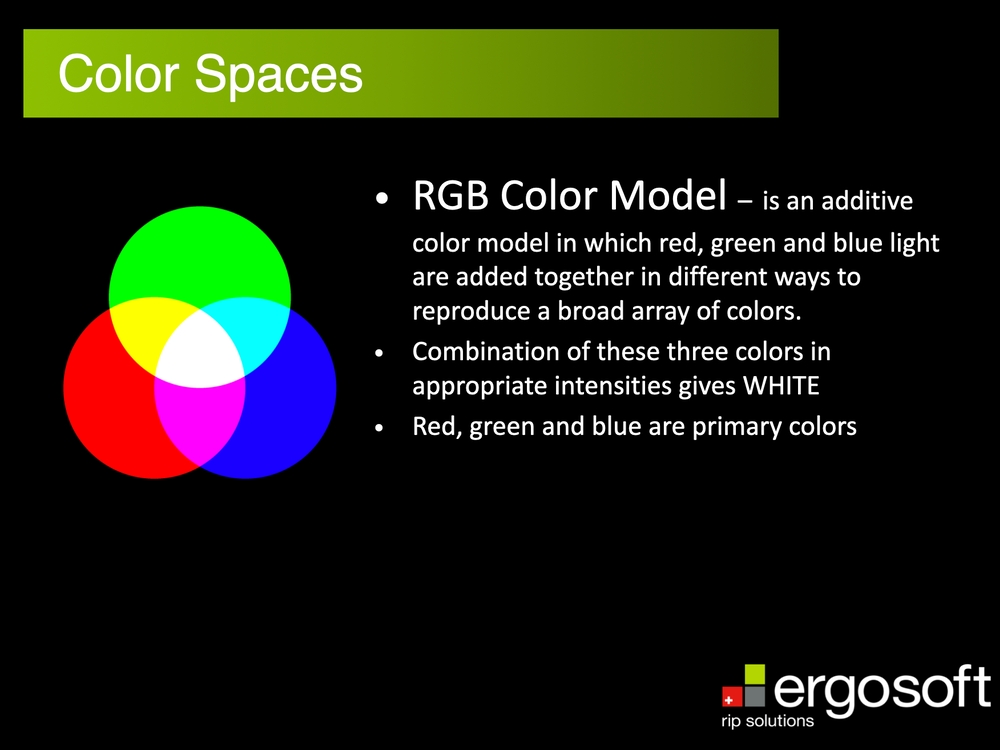
RGB is an additive color space/model in which red, green and blue light are added together in different ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. A combination of these three colors in appropriate intensities gives WHITE. Red, green and blue are primary colors.
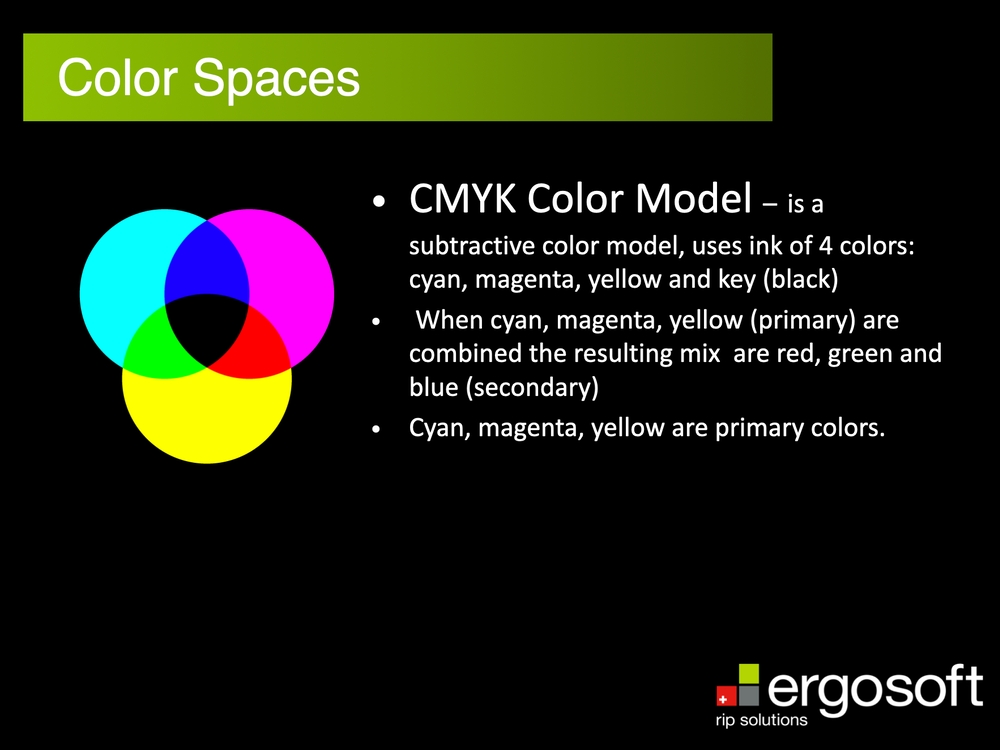
CMYK is a subtractive color space/model. It uses ink of 4 colors: cyan, magenta, yellow and key (black). When cyan, magenta, yellow (primary) are combined the resulting mix are red, green and blue (secondary). Cyan, magenta, yellow are primary colors.
May I help you with sublimation printing in Vietnam?
CMYK stands for cyan, magenta, yellow and black color space/model.
RGB is the color space you see on your computer screens.
CMYK is the color space you see used on your printers.
RGB is an additive color space/model in which red, green and blue light are added together in different ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. A combination of these three colors in appropriate intensities gives WHITE. Red, green and blue are primary colors.
CMYK is a subtractive color space/model. It uses ink of 4 colors: cyan, magenta, yellow and key (black). When cyan, magenta, yellow (primary) are combined the resulting mix are red, green and blue (secondary). Cyan, magenta, yellow are primary colors.
May I help you with sublimation printing in Vietnam?
I recommend using 4 color CMYK for your printer. It is a simpler and more common printer set up and you can achieve enough color variation to print 90% of your work and please the customer.
Four color CMYK consists of cyan, magenta and yellow. If these colors don't give you enough color options then you can add more colors to have more color variations.
See the next picture on this page to see what 8 color CMYK looks like in reality.
Basically you add Lk, Blue, Red and Orange ink along with the cyan, magenta and yellow to get a larger color palette to choose from. Your printer will be able to print a larger number of color variations and hence give you a better image quality - more true to the original color of the image.
Do you need help with sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Four color CMYK consists of cyan, magenta and yellow. If these colors don't give you enough color options then you can add more colors to have more color variations.
See the next picture on this page to see what 8 color CMYK looks like in reality.
Basically you add Lk, Blue, Red and Orange ink along with the cyan, magenta and yellow to get a larger color palette to choose from. Your printer will be able to print a larger number of color variations and hence give you a better image quality - more true to the original color of the image.
Do you need help with sublimation printing in Vietnam?

Understanding Color and Light
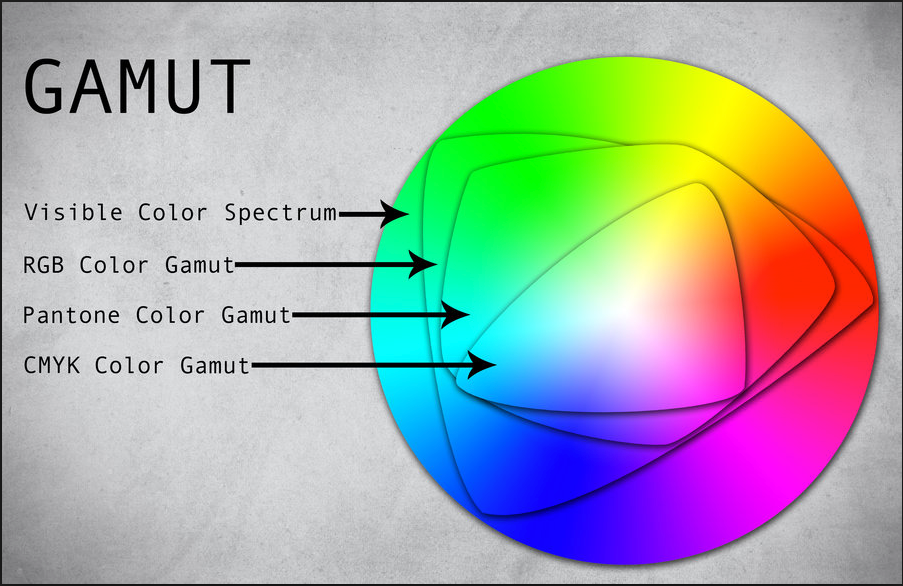
What is a Color Gamut?
A Color Gamut is the range of colors which can be reproduced by any given device (scanner, camera, monitor, printer etc.). Following is a list of representative color systems in order from large to small color gamut. Which color gamut will you use when doing sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Photographic Film
This is one of the best systems available for detecting and reproducing color. Movie-goers are familiar with the difference in color quality between the film projections seen in theaters and the home video versions. This is because the color gamut of film far exceeds that of television.
Laser Light Shows
Lasers can produce very nearly monochromatic light, allowing colors far more saturated than those produced by other systems. However, mixing hues to produce less saturated colors is difficult with lasers.
CRT
CRT (cathode ray tube) and similar video displays have a roughly triangular color gamut which covers a significant portion of the visible color space. In CRTs, the limitations are due to the phosphors in the screen which produce red, green, and blue light only, and then have to be combined to create the desired final color.
Liquid Crystal Display
LCD screens filter the light emitted by a backlight. The gamut of an LCD screen is therefore limited to the emitted spectrum of the backlight. Typical LCD screens use fluorescent bulbs for backlights, and have a gamut much smaller than CRT screens. LCD Screens with certain LED backlights yield a more comprehensive gamut than CRTs.
Television
Television uses a CRT display (usually), but does not take full advantage of its color display properties, due to the limitations of broadcasting. HDTV is far better, but still somewhat less than that of similar products using the same display technology, such as computer monitors.
Paint
Paint mixing, both artistic and for commercial applications, achieves a reasonably large color gamut by starting with a larger palette than the red, green, and blue of CRTs or cyan, magenta, and yellow of printing. Paint may reproduce some highly saturated colors that cannot be reproduced well by CRTs (particularly violet), but overall the color gamut is smaller.
Printing
Sublimation printing in Vietnam uses the CMYK color space (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black). A very few printing processes do not include black; however, those processes are poor at representing low saturation, low intensity colors. Efforts have been made to expand the gamut of the printing process by adding inks of non-primary colors; these are typically orange and green or light cyan and light magenta. Spot color inks of a very specific color are also sometimes used.
The examples above show that ink printing offers a very small color gamut that flounders at the bottom of the gene pool. If you are planning sublimation printing in Vietnam then understanding these basic color theory concepts will help you.
So what is a color gamut gauge and how does it affect sublimation printing in Vietnam?
The human eye can distinguish about 300,000 colors which have been defined by empirical analysis based on Color Mixing. For the color mixing analysis process, three colors are chosen to act as the standard primary colors. A common choice is: red, green and blue. By mixing these primary colors with varying intensities many different colors can be produced. For a given set of primaries the totality of colors that can be produced is called the color gamut. Unfortunately whatever the choice of primary colors the color gamut associated with the primaries can never match the gamut of visible colors using only positive weightings.
The usual standard used as a reference is that produced by the Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage (CIE) in 1931 which defined three primary colors that can be combined additively with no negative coefficients to produce all visible colors.
The CIE model below is very useful as a standard. However because it is based on three imaginary color primaries it is not practical to use in hardware devices. Thus, various other more practical standard color models have been created for everyday use.
Some of the more common color models are:
RGB
The RGB model is the usual method of describing colors on monitors. The actual red, green and blue primaries used depend upon the phosphors used on the monitor. It is not possible to define the complete set of visible colors as defined by the CIE standard with the RGB primaries.
HSB
The HSB model is based upon Hue, Saturation and Brightness. This model allows a more intuitive method of designing a color.
CMYK
The CMYK model is a subtractive model that is used in printing. It uses the subtractive primaries Cyan, Magenta and Yellow. In addition because it is impossible to produce a pure black from these primaries a Black (K) primary is added thus giving the CMYK model. When the gamut of this model is plotted on the CIE diagram it only covers a subset of the interior and will not usually cover the entire monitor gamut either. Thus the image on a monitor can never be completely accurately captured in print. You must understand CMYK if you do sublimation printing in Vietnam?
This demonstrates why the colors of an image on the computer screen never look quite the same as the colors in the final printed image. To try and compensate for this anomaly we use a rendering designed for handling out-of-gamut colors. Out of gamut sublimation printing in Vietnam is possible if your printer uses 8 colors.
Perceptual Rendering
Perceptual rendering attempts to compress the gamut of the source space into the gamut of the destination space in such a way that the overall relationships between the colors (and hence the overall image appearance) is preserved, even though all the colors may change in the process.
Absolute Colorimetric Rendering
Absolute Colorimetric rendering matches those colors in the source space that are inside the gamut of the target space exactly and forces out-of-gamut colors to the nearest reproducible hue, sacrificing lightness and saturation.
Relative Colorimetric Rendering
Relative Colorimetric rendering first scales the white of the source space to the white of the target space, adjusting all other colors relative to that white. Then it matches the adjusted colors in the source space that are inside the gamut of the target space exactly and forces out-of-gamut colors to the nearest reproducible hue, sacrificing lightness and saturation.
Saturation Rendering
Saturation rendering maps fully saturated colors in the source space to fully saturated colors in the target space, sacrificing hue and lightness.
We recommend Perceptual Rendering as the one to use for all your sublimation printing in Vietnam. When using this method the entire gamut of the image is compressed to fit within the gamut of the destination device.
This means that all of the colors that were actually in-gamut will need to be adjusted to make room for the out-of-gamut colors. Moreover, unlike what happens in the saturation rendering processes, with perceptual rendering all pixels are treated with respect for each other. As a result, out-of-gamut pixels may not be moved to the closest reproducible color.
You may think that this adjustment makes every color wrong. That assumption, in fact, is correct. Therefore, it would seem that perceptual rendering processes would make things even worse. But strangely enough that is not the case because all of the colors have been adjusted proportionally, even those that the destination device could accurately reproduce. With perceptual rendering, the chance that a viewer will notice that all of the colors have been modified is minimized. This is the most common rendering intent that is used when converting from RGB to CMYK color space.
RGB vs CMYK
Computer monitors emit color as RGB (red, green, blue) light. Although all colors of the visible spectrum can be produced by merging red, green and blue light, monitors are capable of displaying only a limited gamut (i.e., range) of the visible spectrum.
You will need to understand and use both when sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Whereas monitors emit light, inked paper absorbs or reflects specific wavelengths. Cyan, magenta and yellow pigments serve as filters, subtracting varying degrees of red, green and blue from white light to produce a selective gamut of spectral colors.
Like monitors, printing inks also produce a color gamut that is only a subset of the visible spectrum, although the range is not the same for both. Consequently, the same artwork displayed on a computer monitor may not match that on a printed publication. Also, because printing processes, such as offset lithography use CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) inks, digital art must be converted to CMYK color for print.
Many printers now prefer digital art files be supplied in the RGB color space with ICC profiles attached. Images can then be converted to the CMYK color space by the printer using color management methods that rely on color profiles if present; this helps preserve the best possible detail and vibrancy.
What rendering method is best?
Perceptual Rendering
Perceptual rendering attempts to compress the gamut of the source space into the gamut of the destination space in such a way that the overall relationships between the colors (and hence the overall image appearance) is preserved, even though all the colors may change in the process.
Absolute Colorimetric Rendering
Absolute Colorimetric rendering matches those colors in the source space that are inside the gamut of the target space exactly and forces out-of-gamut colors to the nearest reproducible hue, sacrificing lightness and saturation.
Relative Colorimetric Rendering
Relative Colorimetric rendering first scales the white of the source space to the white of the target space, adjusting all other colors relative to that white. Then it matches the adjusted colors in the source space that are inside the gamut of the target space exactly and forces out-of-gamut colors to the nearest reproducible hue, sacrificing lightness and saturation.
Saturation Rendering
Saturation rendering maps fully saturated colors in the source space to fully saturated colors in the target space, sacrificing hue and lightness.
We recommend Perceptual Rendering as the one to use for all your sublimation printing in Vietnam. When using this method the entire gamut of the image is compressed to fit within the gamut of the destination device.
This means that all of the colors that were actually in-gamut will need to be adjusted to make room for the out-of-gamut colors. Moreover, unlike what happens in the saturation rendering processes, with perceptual rendering all pixels are treated with respect for each other. As a result, out-of-gamut pixels may not be moved to the closest reproducible color.
You may think that this adjustment makes every color wrong. That assumption, in fact, is correct. Therefore, it would seem that perceptual rendering processes would make things even worse. But strangely enough that is not the case because all of the colors have been adjusted proportionally, even those that the destination device could accurately reproduce. With perceptual rendering, the chance that a viewer will notice that all of the colors have been modified is minimized. This is the most common rendering intent that is used when converting from RGB to CMYK color space.
RGB vs CMYK
Computer monitors emit color as RGB (red, green, blue) light. Although all colors of the visible spectrum can be produced by merging red, green and blue light, monitors are capable of displaying only a limited gamut (i.e., range) of the visible spectrum.
You will need to understand and use both when sublimation printing in Vietnam?
Whereas monitors emit light, inked paper absorbs or reflects specific wavelengths. Cyan, magenta and yellow pigments serve as filters, subtracting varying degrees of red, green and blue from white light to produce a selective gamut of spectral colors.
Like monitors, printing inks also produce a color gamut that is only a subset of the visible spectrum, although the range is not the same for both. Consequently, the same artwork displayed on a computer monitor may not match that on a printed publication. Also, because printing processes, such as offset lithography use CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) inks, digital art must be converted to CMYK color for print.
Many printers now prefer digital art files be supplied in the RGB color space with ICC profiles attached. Images can then be converted to the CMYK color space by the printer using color management methods that rely on color profiles if present; this helps preserve the best possible detail and vibrancy.
Best Advice
Start with Tech Packs
Reverse Engineer your MOQs
Choose your QC Levels
Look Up Import Tax
Calculate Shipping Costs
Reverse Engineer your MOQs
Choose your QC Levels
Look Up Import Tax
Calculate Shipping Costs
Services
Consulting
Factory Introductions
Design and Development
A - Z Sublimation Garment Production
Factory Introductions
Design and Development
A - Z Sublimation Garment Production